This article will explain how California's cost of electric vehicles compares to other energy sources. It discusses issues like the cost of supporting electric cars (EVs), and the reliability of our grid. It also discusses the state’s clean energy goals. You'll also learn about the benefits and drawbacks of EVs as well as ways to improve the grid.
California's clean power goals
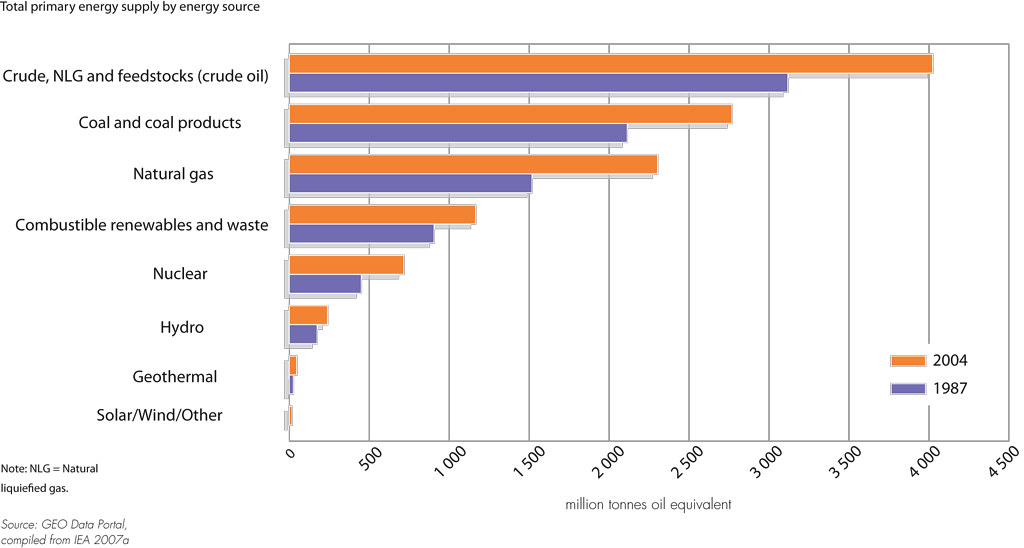
California's clean-energy goals are designed to decrease our dependence upon fossil fuels. Despite our clean energy goals, the state still uses fossil fuels to meet our energy needs. Our state is seventh in oil production, and fourteenth for natural gas production. Our state's clean energy goals will help us achieve our goal to have 100% clean energy by 2045.
California still has a ways to go before we can achieve these goals. But, there are some steps that are already being taken. One of these steps is to make greater use of distributed, sustainable energy sources. California has made considerable investments in solar power and other clean energy resources recently. California intends to produce half its energy from renewable sources by 2025. While lawmakers work on legislation to speed up the transition to cleaner energy, they are also drafting legislation. More than 25 bills are currently pending in the state legislature.

Increasing reliance on renewable resources
California is taking steps to increase its use of solar and wind energy. Renewable energy accounted for 19.8% of California's total electricity generation in 2013. This number is expected rise to 35% in 2030. This will be mainly from solar and wind energy. However, non-hydro sources have increased from just 1 percent in 2005 up to 12.5 percent by 2020. However, the demand for electricity remains relatively stable. Meanwhile, the use of renewable fuels in transportation has risen significantly in recent years, from a mere one percent in 2005 to a nearly doubled rate last year.
California has passed the Renewables Portfolio Standard. This law requires electricity providers to buy renewable energy in order to meet their renewable electricity demands. This law requires electricity providers to purchase at minimum 20 percent of their electricity from renewable sources before 2022. In addition, they must increase the renewable share by one percentage per year.
Supporting EVs: Costs
California's state air resources board has plans to spend $95million by 2019 on various EV-related programs. This money comes from a part of registration fees and profits from cap-andtrade programs. The program is expected offer rebates to EV-owners. However, if a EV is something you're considering purchasing, you should think about the costs involved.
California's major utilities offer two types of EV charging rates. The first rate is for the electricity that EVs consume. The second rate applies for all electricity consumed in a home.
Grid reliability
California's grid reliability problem has been a major concern for many years. California's dependence on outside power is about 20-30 percent of its electricity. This makes its grid highly vulnerable to weather and political changes. The electricity grid is under immense strain due to the increased demand for energy, electric vehicles, and air conditioners.
The state is taking steps to improve grid reliability. The Board of Governors of California Independent System Operator approved the extension of reliability-must-run contracts with four power stations. These agreements will ensure the power plants are operational for the entirety of the agreement, which runs until 2023.